Garbage Collection Statistics
Xdebug's built-in garbage collection statistics profiler allows you to find out when the PHP internal garbage collector triggers, how many variables it was able to clean up, how long it took, and how how much memory was actually freed.
Introduction #
Garbage Collection (GC) in PHP can have a serious impact on memory and performance, so understanding when it is triggered and how efficient each run is, allows you to optimise your programs. The PHP Engine does not provide a mechanism to gather statistics about garbage collection, but Xdebug now does.
For the time being, the garbage collection statistics are collected in a human readable, tabular format only, because there are no tools for this kind of report that we could generate machine readable output for. Future versions may include exports in other formats to allow machine processing.
Usage #
There are two approaches to start collecting the GC statistics with two different use-cases.
By Settings
The first is entirely via INI settings and the primary use-case is to collect statistics for indiviual CLI script runs (where GC is often an issue).
php -dxdebug.mode=gcstats -dxdebug.start_with_request=yes your_script.php
If you wish to collect the garbage collection statistics for every script
that you execute, you can set the xdebug.mode=gcstats and
xdebug.start_with_request=yes INI settings on the system or
directory-level. Be aware that activating the collection globally will produce
an output file for every executed script, even if the garbage
collector didn't run.
By Calling a Function
The second approach to starting collection is to call the function xdebug_start_gcstats() directly in your PHP script. This gives you more control over when statistics collection is started.
You can stop collection for both INI and function based approaches by calling xdebug_stop_gcstats().
Output #
GC status file are written to the directory configured with xdebug.output_dir. The file name can be configured with xdebug.gc_stats_output_name.
The output format of Garbage Collection statistics is a tabular human readable text output.
Garbage Collection Report
version: 1
creator: xdebug 2.6.0 (PHP 7.2.0)
Collected | Efficiency% | Duration | Memory Before | Memory After | Reduction% | Function
----------+-------------+----------+---------------+--------------+------------+---------
10000 | 100.00 % | 0.00 ms | 5539880 | 579880 | 79.53 % | bar
10000 | 100.00 % | 0.00 ms | 5540040 | 580040 | 79.53 % | Garbage::produce
4001 | 40.01 % | 0.00 ms | 2563048 | 578968 | 77.41 % | gc_collect_cycles
The header contains the version of the report and the version of Xdebug that generated it.
The table itself then contains one row for each garbage collection run each with 7 reported variables:
- Collected — The number of so called "roots" that have been garbage collected during this run. A "root" is either an PHP object (instance) or an array that is under observation by the Garbage Collector for potential cleanup.
- Efficiency% — Is the number of cleared roots divided by 10 000 - a magic number of "roots" when reached triggers PHPs internal garbage collector to run automatically.
- Duration — Denotes the duration in milliseconds that this garbage collection run took.
- Memory Before — Contains the memory as measured by
memory_get_usage()before this GC run was activated. - Memory After — Contains the memory as measured by
memory_get_usage()after the GC run was finished. - Reduction% — The percent reduction in memory due to this GC run.
- Function — The name of the function or method the GC run was triggered in. If it is
gc_collect_cycles()then this means the Garbage Collector was triggered explicitly. All other values indicate the GC was triggered implicitly due to the 10 000 "roots" reached metric of the PHP engine.
For details on how PHPs garbage collection works see the PHP manuals chapter on Garbage Collection.
Related Settings and Functions #
- string xdebug.gc_stats_output_name = gcstats.%p
- string xdebug.log =
- integer xdebug.log_level = 7
- string xdebug.mode = develop
- string xdebug.output_dir = /tmp
- string xdebug.start_with_request = default
- xdebug_get_gc_run_count() : int
- xdebug_get_gc_total_collected_roots() : int
- xdebug_get_gcstats_filename() : mixed
- xdebug_info() : mixed
- xdebug_start_gcstats() : mixed
- xdebug_stop_gcstats() : false|string
Settings #
string xdebug.gc_stats_output_name = gcstats.%p #
This setting determines the name of the file that is used to dump garbage collection statistics into. The setting specifies the format with format specifiers, very similar to sprintf() and strftime(). There are several format specifiers that can be used to format the file name.
See the xdebug.trace_output_name documentation for the supported specifiers.
string xdebug.log = #
Configures Xdebug's log file.
Xdebug will log to this file all file creations issues, Step Debugging connection attempts, failures, and debug communication.
Enable this functionality by setting the value to a absolute path. Make sure
that the system user that PHP runs at (such as www-data if you are
running with Apache) can create and write to the file.
The file is opened in append-mode, and will therefore not be overwritten by default. There is no concurrency protection available.
The log file will include any attempt that Xdebug makes to connect to an IDE:
[2693358] Log opened at 2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195 [2693358] [Step Debug] INFO: Connecting to configured address/port: localhost:9003. [2693358] [Step Debug] ERR: Could not connect to debugging client. Tried: localhost:9003 (through xdebug.client_host/xdebug.client_port). [2693358] [Profiler] ERR: File '/foo/cachegrind.out.2693358' could not be opened. [2693358] [Profiler] WARN: /foo: No such file or directory [2693358] [Tracing] ERR: File '/foo/trace.1485761369' could not be opened. [2693358] [Tracing] WARN: /foo: No such file or directory [2693358] Log closed at 2020-09-02 07:19:09.617510
It includes the opening time (2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195), the
IP/Hostname and port Xdebug is trying to connect to
(localhost:9003), and whether it succeeded (Connected to
client). The number in brackets ([2693358]) is the
Process ID.
It includes:
[2693358]- process ID in brackets
2020-09-02 07:19:09.616195- opening time
For Step Debugging:
INFO: Connecting to configured address/port: localhost:9003. ERR: Could not connect to debugging client. Tried: localhost:9003 (through xdebug.client_host/xdebug.client_port).
For Profiling:
ERR: File '/foo/cachegrind.out.2693358' could not be opened. WARN: /foo: No such file or directory
For Function Trace and Flame Graphs:
ERR: File '/foo/trace.1485761369' could not be opened. WARN: /foo: No such file or directory
All warnings and errors are described on the Description of errors page, with
detailed instructions on how to resolve the problem, if possible. All errors are always logged through
PHP's internal logging mechanism (configured with error_log
in php.ini). All warnings and errors also show up in the
diagnostics log that you can view by calling xdebug_info().
Step Debugger Communication
The debugging log can also log the communication between Xdebug and an IDE.
This communication is in XML, and starts with the <init XML
element:
<init
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.org/dbgp/xdebug"
fileuri="file:///home/httpd/www.xdebug.org/html/router.php"
language="PHP" xdebug:language_version="7.4.11-dev"
protocol_version="1.0" appid="2693358" idekey="XDEBUG_ECLIPSE">
<engine version="3.0.0-dev"><![CDATA[Xdebug]]></engine>
<author><![CDATA[Derick Rethans]]></author>
<url><![CDATA[https://xdebug.org]]></url>
<copyright><![CDATA[Copyright (c) 2002-2020 by Derick Rethans]]></copyright>
</init>
The fileuri attribute lists the entry point of your
application, which can be useful to compare to breakpoint_set
commands to see if path mappings are set-up correctly.
Beyond the <init element, you will find the configuration of
features:
<- feature_set -i 4 -n extended_properties -v 1
-> <response
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.org/dbgp/xdebug"
command="feature_set" transaction_id="4" feature="extended_properties" success="1">
</response>
<- step_into -i 9
-> <response
xmlns="urn:debugger_protocol_v1" xmlns:xdebug="https://xdebug.org/dbgp/xdebug"
command="step_into" transaction_id="9"
status="break" reason="ok">
<xdebug:message filename="file:///home/httpd/www.xdebug.org/html/router.php" lineno="3">
</xdebug:message>
</response>
You can read about DBGP - A common debugger protocol specification at its dedicated documation page.
The xdebug.log_level setting controls how much information is logged.
Many Linux distributions now use systemd, which
implements private tmp directories. This means that when PHP
is run through a web server or as PHP-FPM, the /tmp directory is
prefixed with something akin to:
/tmp/systemd-private-ea3cfa882b4e478993e1994033fc5feb-apache.service-FfWZRg
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
integer xdebug.log_level = 7 #
Configures which logging messages should be added to the log file.
The log file is configured with the xdebug.log setting.
The following levels are supported:
| Level | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Criticals | Errors in the configuration |
| 1 | Errors | Connection errors |
| 3 | Warnings | Connection warnings |
| 5 | Communication | Protocol messages |
| 7 | Information | Information while connecting |
| 10 | Debug | Breakpoint resolving information |
Criticals, errors, and warnings always show up in the diagnostics log that you can view by calling xdebug_info().
Criticals and errors are additionally logged through
PHP's internal logging mechanism (configured with error_log
in php.ini).
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
string xdebug.mode = develop #
This setting controls which Xdebug features are enabled.
This setting can only be set in php.ini or
files like 99-xdebug.ini that are read when a PHP process starts
(directly, or through php-fpm). You can not set this value in
.htaccess and .user.ini files, which are read
per-request, nor through php_admin_value as used in Apache VHOSTs
and PHP-FPM pools.
The following values are accepted:
off- Nothing is enabled. Xdebug does no work besides checking whether functionality is enabled. Use this setting if you want close to 0 overhead.
develop- Enables Development Helpers including the overloaded var_dump().
coverage- Enables Code Coverage Analysis to generate code coverage reports, mainly in combination with PHPUnit.
debug- Enables Step Debugging. This can be used to step through your code while it is running, and analyse values of variables.
gcstats- Enables Garbage Collection Statistics to collect statistics about PHP's Garbage Collection Mechanism.
profile- Enables Profiling, with which you can analyse performance bottlenecks with tools like KCacheGrind.
trace- Enables the Function Trace and Flame Graphs features.
- The former allows you record every function call, including arguments, variable assignment, and return value that is made during a request to a file.
- The latter can be used to visualise certain performance characteristics.
You can enable multiple modes at the same time by comma separating their
identifiers as value to xdebug.mode: xdebug.mode=develop,trace.
XDEBUG_MODE environment variable
You can also set Xdebug's mode by setting the XDEBUG_MODE
environment variable on the command-line; this will take precedence over the
xdebug.mode setting, but will not change the value of the xdebug.mode
setting.
Some web servers have a configuration option to
prevent environment variables from being propagated to PHP and Xdebug.
For example, PHP-FPM has a clear_env
configuration setting that is on by default, which you will
need to turn off if you want to use XDEBUG_MODE.
Make sure that your web server does not clean the environment, or specifically
allows the XDEBUG_MODE environment variable to be passed on.
string xdebug.output_dir = /tmp #
The directory where Xdebug will write tracing, profiling, and garbage collection statistics to. This directory needs to be writable for the system user with which PHP is running.
This setting can be changed in php.ini, .htaccess
(and equivalent files), and within a PHP file with ini_set().
In some cases (when profiling, or when
xdebug.start_with_request=yes with tracing), Xdebug
creates the file before the script runs. In that case, changes made through
ini_set() will not be taken into account.
This setting can additionally be configured through the
XDEBUG_CONFIG
environment variable.
Many Linux distributions now use systemd, which
implements private tmp directories. This means that when PHP
is run through a web server or as PHP-FPM, the /tmp directory is
prefixed with something akin to:
/tmp/systemd-private-ea3cfa882b4e478993e1994033fc5feb-apache.service-FfWZRg
string xdebug.start_with_request = default #
Step Debugging, a Function Trace, Flame Graphs, Garbage Collection Statistics, or Profiling can be activated at the start of a PHP request. Whether this happens depends on the value of this setting:
yes-
The functionality starts when the PHP request starts, and before any PHP code is run.
For example xdebug.mode=
traceand xdebug.start_with_request=yesstarts a Function Trace for the whole request. no-
The functionality does not get activated when the request starts.
You can still start a Function Trace with xdebug_start_trace(), or Garbage Collection Statistics with xdebug_start_gcstats().
Step Debugging and Profiling will never activate with this value.
trigger-
The functionality only gets activated when a specific trigger is present when the request starts.
The name of the trigger is
XDEBUG_TRIGGER, and Xdebug checks for its presence in either$_ENV(environment variable),$_GETor$_POSTvariable, or$_COOKIE(HTTP cookie name).There is a legacy fallback to a functionality specific trigger name:
XDEBUG_PROFILE(for Profiling),XDEBUG_TRACE(for a Function Trace or Flame Graphs), andXDEBUG_SESSION(for Step Debugging).There is another legacy trigger for Step Debugging only. If you set the
XDEBUG_CONFIGenvironment variable to any value, then the step debugger will also get activated.Debug session management for Step Debugging is also available through
XDEBUG_SESSION_START.With xdebug.trigger_value you can control which specific trigger value will activate the trigger. If xdebug.trigger_value is set to an empty string, any value will be accepted.
In this mode it is also possible to activate Step Debugging with xdebug_break().
default-
The
defaultvalue depends on xdebug.mode:- debug:
trigger - gcstats:
no - profile:
yes - trace:
trigger
- debug:
Functions #
xdebug_get_gc_run_count() : int #
Returns the number of garbage collection runs that have been triggered so far
The function returns the number of times the garbage collection has been triggered in the currently running script.
This number is available even if the xdebug.start_with_request INI setting is
not set to yes.
xdebug_get_gc_total_collected_roots() : int #
Returns the number of variable roots that have been collected so far
The function returns the number of variable roots that the garbage collection has collected during all runs of the garbage collector in the current script.
This number is available even if the xdebug.start_with_request INI setting is
not set to yes.
xdebug_get_gcstats_filename() : mixed #
Returns the garbage collection statistics filename
Returns the name of the file which is used to save garbage collection
information to, or false if statistics collection is not active.
xdebug_info( string $category = null ) : mixed #
Show and retrieve diagnostic information
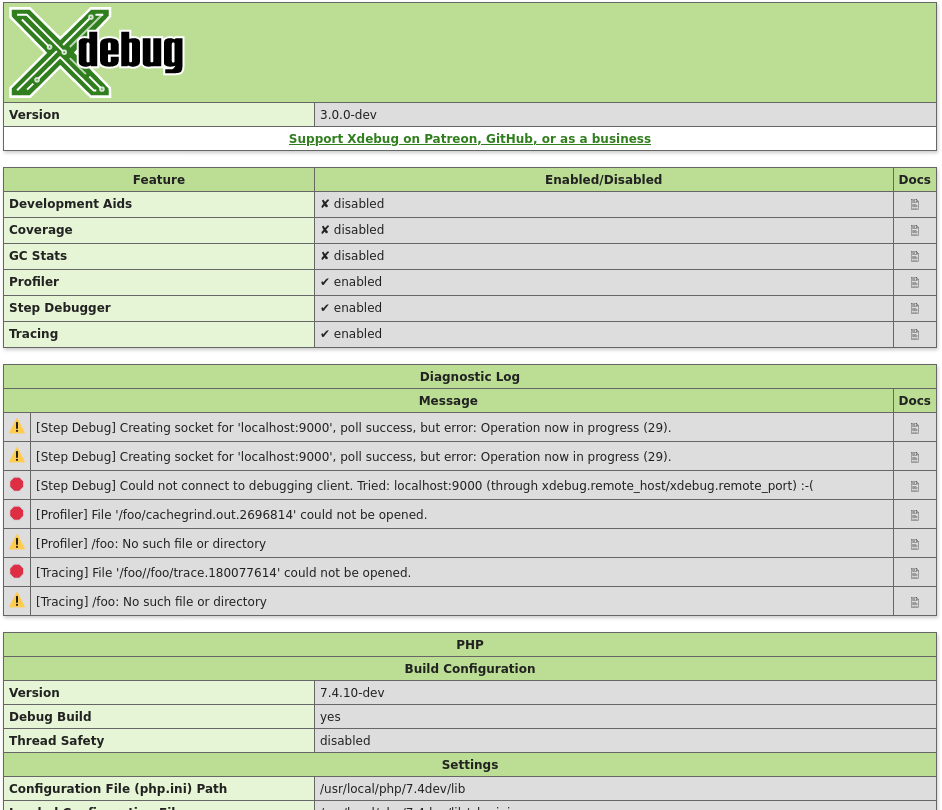
This function presents APIs to retrieve information about Xdebug itself. Which information gets returned, or displayed, depends on which arguments, or none at all, are given.
$category =
Without arguments, this function returns an HTML page which shows diagnostic information. It is analogous to PHP's phpinfo() function.
The HTML output includes which mode is active, what the settings are, and diagnostic information in case there are problems with debugging connections, opening of files, etc.
Each warning and error in the diagnostics log also links through to the Description of errors documentation page.
$category = 'mode' (New in Xdebug 3.1)
The function returns an array of all the
enabled modes, whether through xdebug.mode or the
XDEBUG_MODE environment variable.
Example:
<?php
var_dump( xdebug_info( 'mode' ) );
?>Returns:
array(3) {
[0] =>
string(5) "debug"
[1] =>
string(7) "develop"
[2] =>
string(5) "trace"
}
$category = 'extension-flags' (New in Xdebug 3.1)
The function returns an array of all the compile flags that were enabled when
running ./configure as part of Xdebug's compilation process, and
all the system-specific detected features that effect Xdebug's behaviour.
If the compression flag is enabled, then the xdebug.use_compression
setting is available, and enabled by default.
Profiling and Function Trace will create GZip compressed files if the xdebug.use_compression setting is turned on (the default).
If the control-socket and tsc elements are present,
then Xdebug can be controlled with the Xdebug Control tool, as long as
xdebug.control_socket is not set to "off".
If the control-socket flag is present, but the tsc
flag is not present, then you must set xdebug.control_socket to
"time" deliberately for Xdebug Control to be able to interact
with Xdebug.
Example:
<?php
var_dump( xdebug_info( 'extension-flags' ) );
?>Returns:
array(1) {
[0] =>
string(11) "compression"
[1] =>
string(14) "control-socket"
[2] =>
string(3) "tsc"
}
xdebug_start_gcstats( ?string $gcstatsFile = null ) : mixed #
Start the collection of garbage collection statistics
Start tracing garbage collection attempts from this point to the file in the gcstatsFile parameter. If no filename is given, then garbage collection stats file will be placed in the directory as configured by the xdebug.output_dir setting.
In case a file name is given as first parameter, the name is relative to the current working directory. This current working directory might be different than you expect it to be, so please use an absolute path in case you specify a file name. Use the PHP function getcwd() to figure out what the current working directory is.
If xdebug.start_with_request=yes, then filename depends on the
xdebug.gc_stats_output_name setting.
The full path and filename to which Xdebug collects statistics into is returned from this function. This will be either the filename you pass in, or the auto generated filename if no filename has been passed in.
xdebug_stop_gcstats() : false|string #
Stops the current garbage collection statistics collection
Stop garbage collection statistics collection and closes the output file.
The function returns the filename of the file where the statistics were written to.